A site map (or sitemap) is a list of pages aimed to aid visitors and web crawlers find the different sections on your website. It can either be an HTML sitemap which is designed for users so they can easily browse the contents, or an XML version that is intended for bots so they can include every part of your site to their search engine index. We’ll talk about XML sitemaps on this post.
Table of Contents
- Definition and Importance of an XML Sitemap
- Sitemap Usage
- Protocol, Formats and Types
3.1 Sitemap Protocol
3.2 Sitemap Index File
3.3 File Formats
3.4 File Types Based on Content and Device
- Image Sitemap
- Video Sitemap
- News Sitemap
- Mobile Sitemap
- Web-based and Downloadable Sitemap Generators
- How To Submit An XML Sitemap
5.1 Submit Sitemap via an HTTP Request
5.2 Submit Sitemap through Robots.txt
5.3 Submit Sitemap via Webmaster Tools
- Google Webmaster Tools
- Bing Webmaster Tools
- XML Sitemap Best Practices
»Definition and Importance of an XML Sitemap
One significant task when you perform an SEO Audit Checklist is to submit an XML Sitemap. In simple terms, an XML sitemap or an Extensible Markup Language sitemap is a map of your site. It contains the overall structure, sections, links and information about all the pertinent URLs found on your website. It is basically submitted to Google and Bing so they can:
- quickly navigate around your site
- add your pages to their index
- be immediately informed about any changes made on your website
- understand which among the pages are most important
- improve your visibility on search results
- help you discover broken links or orphaned pages within your site
»Sitemap Usage
Sitemaps are especially useful if your site:
- has dynamic content
- has rich AJAX, Flash, scripts, videos or photos on the page
- is relatively new and has built minimal internal and external links
- has a large directory of archived content yet no good internal linking structure to active pages
»Protocol, File Formats and Types
Sitemap Protocol.
An XML sitemap follows a data protocol as stated on Sitemaps.org.
Required/optional tags for a sitemap file:
- should begin with an opening <urlset> tag and end with a closing </urlset> tag
- should specify the namespace (protocol standard) within the <urlset> tag
- should include a <url> entry for each URL, as a parent XML tag
- should include a <loc> child entry for each <url> parent tag
- <lastmod>, <changefreq>, <priority> tags are optional.
Here’s an example. Items in italics are optional.
Each sitemap file has the following limitations:
- must have no more than 50,000 URLs
- must be no larger than 10MB (10,485,760 bytes)
Sitemap Index File.
For large sites (e.g. e-commerce sites) that do not meet the usual requirements, a sitemap index may be used.
Required/optional tags for a sitemap index file:
- should begin with an opening <sitemapindex> tag and end with a closing </sitemapindex> tag
- should include a <sitemap> entry for each Sitemap as a parent XML tag.
- should include a <loc> child entry for each <sitemap> parent tag.
- <lastmod> tag is optional.
Here’s an example:
File Formats.
Google and Bing supports the following file formats for a sitemap:
- XML format based on the Sitemap protocol
- RSS, mRSS and Atom 1.0 (for Google)
- Text file (for Google)
File Types Based On Content and Device.
Google supports specialized sitemaps based on the content type and device used on your website.
-
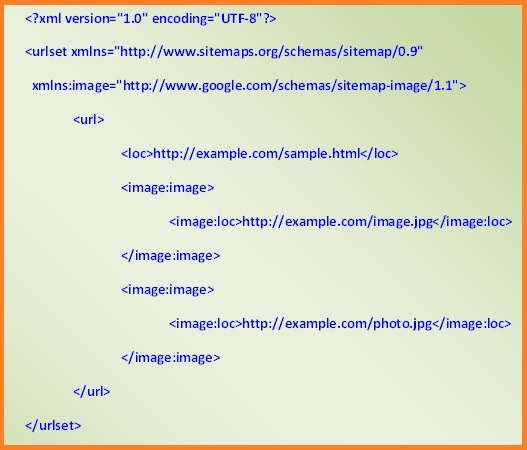
Image Sitemap.
As image search is separate from web search, it then equally important to create and submit an image sitemap. For each URL you list, note the essential images on that page. You can record up to 1,000 images for each page.
Required/optional tags:
-should begin with an opening <image:image> tag and end with a closing </image:image> tag
-should include a <image:loc> child entry for each <image:image> parent tag
-<image:caption>, <image:geo_location>, <image:title>, <imagelicense> tags are optional.
-
Video Sitemap.
For video sitemaps, you can either add video information to an existing sitemap or generate an mRSS feed for your site and submit the feed as a sitemap. Each video sitemap or mRSS feed file that you provide must be under 50MB in size when uncompressed, and can contain no more than 50,000 video items. If it exceeds the usual limit, you can submit multiple Sitemaps and a Sitemap index file. Read more about the video-specific tags and protocols as recommended by Google Webmaster Tools.
-
News Sitemap.
This is a special file that allows Google News to discover, crawl and index all news articles faster; extract and display article information and characterize content more accurately; and annotate them with meta data. Learn the protocols and news-specific tags here.
-
Mobile Sitemap.
This is similar to the web sitemap except for a specific tag and additional namespace requirement.
»Web-based and Downloadable Sitemap Generators
If you’re an SEO company or an Internet/Digital Marketing agency, it would be a great practice to make use of tools and sitemap generators available over the web to easily facilitate the sitemap creation. Here are a few free and paid options:
1. Sitemap Generator by XML-Sitemaps.com. Build sitemap online in different formats: XML, text, ROR, HTML.
2. Google Sitemap Generator Tool by Internet Marketing Ninjas. Generate Sitemaps over the internet in XML, Excel and HTML formats. Additional Reports include: Internal Page, External Links, Internal/External Redirects, Internal/External Errors Reports.
3. Google Sitemap Generator for Windows by GSiteCrawler. Download and Install on your Windows unit.
4. A1 Sitemap Generator 4.2.0 by Micro-Sys ApS. Download for free, fully functional with a 30-day evaluation period, format includes: HTML, XML, image, video.
5. Google XML Sitemaps, Image XML-Sitemap Generator and Google XML Sitemap for Videos, WordPress Plugins. Install these plugins if your website platform is WordPress.
»How to Submit an XML Sitemap
There are mainly three ways to submit an XML sitemap to search engines.
How to Submit Sitemap via an HTTP Request.
Type this line to your browser’s address bar. Use the following format:
For Google:
http://www.google.com/webmasters/tools/ping?sitemap=http://www.YourURL.com/sitemap.xml
For Bing:
http://www.bing.com/webmaster/ping.aspx?sitemap=www.YourURL.com/sitemap.xml
How to Submit Sitemap through Robots.txt.
Insert a line on your robots.txt file, typically at the end of the file, referencing the location of your sitemap.
Example:
Sitemap: http://www.YourURL.com/sitemap.xml
How to Submit Sitemap via Webmaster Tools
Google Webmaster Tools.
1. Verify that you own the website via Google Webmaster Tools.
- Sign in to Google Webmaster Tools.
- Type in your website.
- Either copy the meta tag indicated or download the HTML verification file.
Example of meta tag:
<meta name=”google-site-verification” content=”z5mJLjVGtEe5qzCefW1pamxI7H46u19n4XnxEzgl1AU” />
- Insert the meta tag on your homepage header or upload the HTML file on the root directory.
- Once done, go back to Google Webmaster Tools and click verify.
2. Once verified, head over to Site configuration and choose Sitemaps.
3. Enter your sitemap URL: http://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
4. Submit.
Bing Webmaster Tools.
1. Sign in to Bing Webmaster Tools.
2. Use Sitemaps Tool. Paste the sitemap URL into the Direct Sitemap Submission text box.
3. Click Submit.
»XML Sitemaps Best Practices
Here are some of the best practices to follow to ensure that your sitemaps are well crawled and submitted:
1. Adhere to the Sitemap guidelines:
- Must be UTF-8 encoded
- URLs must be URL-escaped and encoded
- Required tags such as namespace must always be indicated.
2. Know the limits.
- For a generic XML sitemap, must not have more than 50,000 URLs and not larger than 10MB.
- For an image sitemap, enlist up to 1,000 images per page.
- For a video sitemap, must be under 50MB in size when uncompressed, and can contain no more than 50,000 video items
If it exceeded the above limits, use Sitemap Index File instead.
3. On using Sitemap Index file, remember to upload the referenced multiple sitemaps under the same root domain.
4. For image sitemaps, including <image:title> tag is a must.
5. Validate before going live. Use W3C XML Validator.
6. Always upload at the root folder of your website.
7. Make it a habit to regularly check your Webmaster Tools for crawl results.
References:
http://www.sitemaps.org/protocol.html http://www.internetmarketingninjas.com/blog/search-engine-optimization/the-ultimate-guide-to-xml-sitemaps http://support.google.com/webmasters/bin/topic.py?hl=en&topic=20986&parent=8476&ctx=topic http://support.google.com/webmasters/bin/answer.py?hl=en&answer=156184 http://support.google.com/webmasters/bin/answer.py?hl=en&answer=183668&ctx=cb&src=cb&cbid=1gkdr7vlcoxwn&cbrank=1 http://www.bing.com/blogs/site_blogs/b/webmaster/archive/2009/08/15/uncovering-web-based-treasure-with-sitemaps-sem-101.aspx http://www.webconfs.com/importance-of-sitemaps-article-17.php